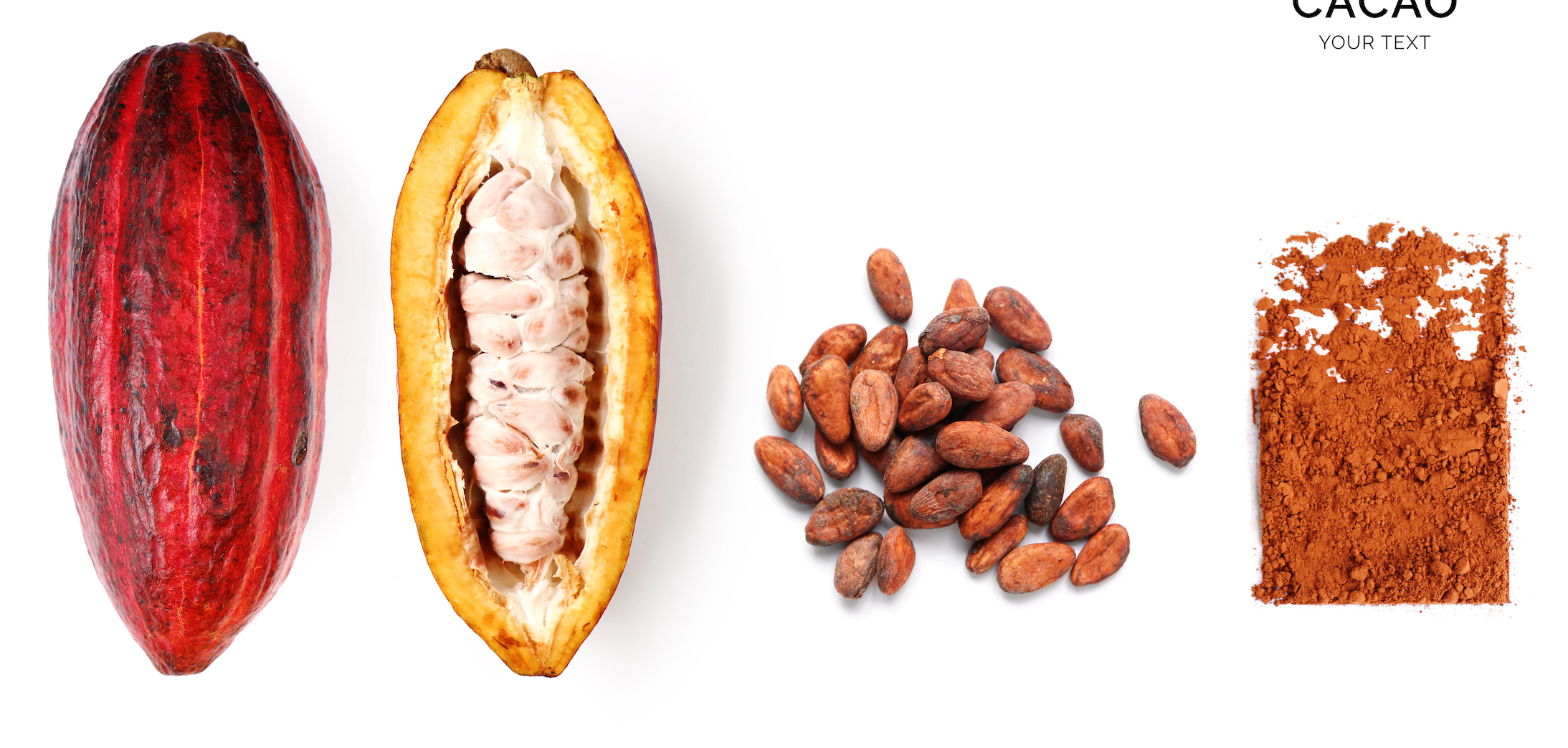
Cocoa is a botanical powerhouse with a complex array of naturally occurring compounds valued by both chefs and wellness seekers.
But not all cocoa is created equal. The journey from bean to finished product involves choices that can significantly impact its nutritional integrity. Understanding these differences helps you choose the most nutrient-rich, health-supportive form of cocoa.
Key Takeaways:
- Mushroom cocoa blends cacao with functional mushrooms to support relaxation and recovery.
- Raw cacao and minimally processed cocoa retain more nutrients than alkalized versions.
- Mushrooms such as Reishi, Tremella, and Poria gently support mood modulation, immunity, and overall recovery—ideal for winding down and recharging.
- Prioritize raw or minimally processed cacao with transparent sourcing for maximum nutritional value.
Cocoa vs. Cacao: What’s the Difference?
Though they come from the same source—the Theobroma cacao tree—cocoa and cacao differ in how they're processed. That distinction shapes everything from flavor to the presence of naturally occurring compounds.
Cacao
- Refers to raw or minimally processed beans.
- Typically fermented and dried, but not roasted.
- May retain more of the bean’s natural compounds, such as flavonoids, which are plant compounds with antioxidant properties.
- Has a more intense, bitter flavor.
Cocoa
- Made from beans that have been roasted and further processed.
- Develops a smoother and more mellow taste, creating the familiar chocolate flavor.
- Some naturally occurring compounds and antioxidants are reduced due to heat exposure.
Cacao is less processed, retaining more of its original compounds and complexity. Cocoa is further processed—roasted and often alkalized—resulting in a smoother taste but reduced antioxidant levels. Both have purpose—whether you’re after deeper nutritional value or a softer, more classic taste.
At MOGU, we use pure, unprocessed organic cacao in our blends. It’s rich in magnesium and calming flavonoids, supporting nervous system recovery and a deeper sense of calm.
Understanding Cocoa: Types and Processing Methods
Cocoa’s journey from tree to table is one of transformation, shaped by careful craftsmanship at every step. By understanding the different processing methods, we gain insight into how flavor, texture, and the bean’s natural elements evolve, helping us make more intentional choices about the cocoa we enjoy.
How Cocoa Is Made: From Bean to Powder
All cocoa begins with the Theobroma cacao tree, whose pods contain the seeds, commonly known as cacao beans. Transforming these beans into cocoa powder involves several essential steps:
- Harvesting: Ripe cacao pods are hand-harvested and opened to reveal the beans, surrounded by a sweet, white pulp.
- Fermentation: The beans and pulp are left to ferment for several days. This step initiates chemical changes that reduce bitterness and begin to develop the rich flavor we associate with chocolate. It’s a foundational process that’s generally gentle on the bean’s naturally occurring compounds.
- Drying: The beans are dried in the sun to halt fermentation and prepare them for further processing.
- Roasting: Primarily used in the production of cocoa. Roasting enhances flavor, producing the familiar chocolatey notes loved in traditional cocoa. However, it also exposes the beans to heat, which might reduce the presence of certain heat-sensitive compounds like flavanols.
- Grinding and Pressing: Once roasted, the beans are ground into a thick paste (known as cocoa liquor), which is then pressed to separate cocoa solids from cocoa butter.
- Alkalization (Dutch Processing): Some cocoa powders undergo alkalization, a process that treats the cocoa with an alkaline solution. This softens acidity and creates a darker, smoother powder, but it can also significantly reduce naturally occurring flavanols. Hence raw and unalkalized cacao powder is the preferred choice for maximum benefits.
How Cocoa Processing Affects Nutritional Value
While all cocoa begins with the same seed, the path it takes during processing shapes more than just its flavor; it can also influence the presence of naturally occurring compounds. These subtle changes often come down to temperature, pH, and time.
Here’s how different stages of processing affect the nutritional makeup of cocoa:
- Heat Sensitivity of Flavanols: Flavanols, a group of polyphenols naturally found in the cacao bean, are particularly sensitive to heat. Roasting, though key to developing cocoa’s deep flavor and aroma, might reduce the concentration of these compounds. The degree of loss can vary depending on temperature and duration.
- Alkalization and pH Shift: Dutch processing changes the pH of cocoa, creating a smoother, less acidic profile. However, this shift can alter the structure of some beneficial compounds, reducing their levels in the final product. While alkalization deepens color and smooths taste, it significantly reduces flavanol content—one of cocoa’s most valuable compounds.
-
Processing and Bioavailability: While some nutrients may diminish through heat or pH adjustments, others can become more bioavailable or easier to digest. The interplay between preservation and accessibility is complex, and “more” isn’t always “better”—what the body can absorb matters, too.
Rather than viewing cocoa as “healthy” or “not,” it’s more useful to understand how each method of processing involves trade-offs. Less-processed options may retain more of their original complexity and benefits, while traditional cocoa offers consistency, comfort, and broad culinary versatility.
Mushroom Cocoa: A Fusion of Flavor and Function
Mushroom cocoa blends rich, comforting cacao with functional mushrooms such as Reishi, Poria, Tremella, and Lion’s Mane, offering a calming, nutrient-dense way to unwind and recover.
What Is Mushroom Cocoa?
At its core, mushroom cocoa is a blend of cocoa powder and powdered extracts from functional mushrooms such as Reishi, Poria, Tremella, Chaga, and Cordyceps. These mushrooms have long been used in traditional practices and are often known for their adaptogenic properties—helping the body respond to occasional stress and maintain balance.
This combination brings a new dimension to cocoa—pairing indulgent flavor with thoughtful ingredients.
How Is Mushroom Cocoa Made?
Making mushroom cocoa begins with selecting high-quality ingredients.
- Mushrooms are hand-picked, then dried and ground into a fine powder to maximize extraction of beneficial compounds.
- Using filtered water and pressure cookers, the powder is heated to break down the tough chitin cell walls—releasing key bioactive compounds like polysaccharides and beta-glucans.
- Depending on the mushroom, the extraction process uses water, alcohol, or both to draw out the most beneficial compounds.
- After separation and spray-drying, the mushroom extract powders are sieved and carefully blended with cocoa to create a balanced flavor and functional profile.
The Health Benefits of Mushroom Cocoa
Mushroom cocoa goes beyond flavor—combining the functional benefits of mushrooms with the natural comfort of cocoa. The result is a blend that supports physical recovery and mental ease, making it a thoughtful choice for unwinding and recharging.
Nutritional Benefits of Cocoa
Beyond its rich taste, cocoa is packed with naturally occurring compounds that have been valued in wellness practices for centuries.
- Magnesium: Supports normal muscle function and may play a role in promoting relaxation and recovery after physical exertion.
- Flavanols: Linked to circulatory support and cognitive clarity, and a calm, relaxed state. While levels vary depending on how cocoa is processed, flavanols remain a hallmark of the cacao bean and contribute to its soothing properties.
-
Theobromine: A gentle stimulant related to caffeine that promotes a calm, sustained alertness without the sharp spikes and crashes.
Many also choose cocoa in the evening as part of a calming ritual, whether as a warm drink or a soothing dessert element. Its naturally occurring compounds, especially when paired with warm milk or plant-based alternatives, can help set the stage for winding down.
In MOGU’s Cacao Blend, ceremonial-grade cacao is paired with medicinal mushrooms to promote nervous system recovery and deeper rest. This restful, restorative drink helps ease tension, aids in muscle recovery, and sets the stage for sound, restorative sleep.
The Role of Medicinal Mushrooms in Cocoa
When functional mushrooms are added to cocoa, they contribute bioactive compounds that support multiple areas of health and wellness. While their historical use spans centuries, modern research is increasingly validating many of their benefits:
- Reishi: Long associated with calm and balance, Reishi has been studied for its ability to support the body’s stress response and parasympathetic nervous system. Traditionally used to promote rest, emerging research suggests it helps regulate cortisol levels and improve sleep onset.
- Chaga: Contains high levels of polyphenols and melanin, compounds shown to support antioxidant activity and cellular protection. Recent research highlights its role in reducing oxidative stress and promoting immune system function.
- Cordyceps: Supports natural energy production by enhancing ATP synthesis and improving oxygen utilization. Clinical studies suggest measurable improvements in endurance, aerobic capacity, and overall physical performance.
- Lion’s Mane: Contains compounds shown to stimulate Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), which plays a key role in cognitive function. Research suggests benefits for memory, mental clarity, and overall brain health.
- Poria: Supports emotional regulation and rest by modulating neurochemical pathways linked to mood and sleep. Recent findings point to its potential in reducing mental fatigue and promoting a more balanced emotional state.
- Tremella: Helps retain moisture at the cellular level, supporting skin hydration, elasticity, and joint health. Its polysaccharides have been shown to aid in collagen production and enhance antioxidative defense.
Adaptogens and Antioxidants: A Nutrient-Rich Duo
Combining cocoa with functional mushrooms brings together antioxidants and adaptogens—two powerful elements often recognized for their role in supporting the body’s stress response, immune balance, and long-term vitality.
- Adaptogens: Many functional mushrooms, such as Reishi and Cordyceps, are considered adaptogens—natural substances believed to help the body adapt to stress and support long-term resilience.
-
Antioxidants: Those from cocoa flavanols and mushroom compounds play a role in protecting cells from oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
This combination offers a satisfying way to enjoy rich flavor with added support for calm, cognitive clarity, or recovery.
Mushroom Cocoa vs. Regular Cocoa: Which Is Healthier?
Both mushroom cocoa and regular cocoa have their own strengths, but when it comes to overall impact, there are key differences worth considering, especially in terms of nutrition and functional benefits.
Differences in Nutritional Content
While both forms of cocoa provide some of the same foundational benefits, mushroom cocoa adds an extra layer of nutrients thanks to the inclusion of medicinal mushrooms.
Regular Cocoa
- Rich in flavanols, which are associated with cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
- Provides minerals like magnesium, essential for muscle function and relaxation.
- Contains theobromine, a mild stimulant that can help improve mood and focus without the jitters associated with caffeine.
- Naturally rich in antioxidants, especially in minimally processed forms, which tend to retain higher levels of these beneficial compounds.
Mushroom Cocoa
- Contains all of the above benefits from regular cocoa, plus the added advantages of medicinal mushrooms.
- Tremella enhances hydration, supports collagen production, and promotes cellular vitality.
- Poria contributes to digestive health, supports nervous system balance, and encourages restful sleep.
- Reishi offers support for immune function, helps regulate cortisol levels, and promotes emotional balance.
Which Offers More Health Benefits?
While both regular cocoa and mushroom cocoa are nutrient-rich and beneficial in their own right, mushroom cocoa provides a broader spectrum of support. The key difference comes from the adaptogenic properties of the medicinal mushrooms, which may help the body manage stress, promote recovery, and support deeper rest.
- Regular cocoa: Excellent for boosting mood, supporting heart health, and promoting relaxation. However, it doesn’t specifically address areas like stress resilience, immune health, or digestion.
- Mushroom cocoa: Combines the benefits of traditional cocoa with the added power of medicinal mushrooms like Reishi, Tremella, Poria, and Lion’s Mane, which help the body better cope with stress, promote deeper sleep, and support the body’s natural restoration process. These functional mushrooms are not only about flavor—they provide specific benefits that can enhance long-term well-being.
So, if you're looking for a functional drink that nourishes both body and mind with holistic support for stress reduction, sleep quality, and immune health, mushroom cocoa offers broader benefits.
How to Choose the Healthiest Mushroom Cocoa
Choosing the healthiest mushroom cocoa means considering the quality of both the cocoa and the mushrooms used in the blend. To ensure you're getting the most nourishing product, here are a few key factors to look for when selecting your mushroom cocoa.
What to Look for on the Label
- Cocoa Content: Choose products with a high percentage of cocoa solids (70% or higher) and minimal added sugars to maximize health benefits.
- Label Transparency: Look for blends that specify mushroom types (like Reishi, Tremella, and Poria), extract ratios, and levels of key active compounds for full transparency and potency. These details matter—they indicate potency, purity, and how effectively the mushrooms can deliver their intended benefits.
-
Processing Methods: Opt for raw or minimally processed cocoa and mushrooms to preserve their natural compounds and nutritional value.
By keeping these points in mind, you can make a more informed choice and enjoy the full benefits of mushroom cocoa. MOGU’s Cacao PM Blend brings together ceremonial cacao and medicinal mushrooms like Reishi to support relaxation, muscle recovery, and the body’s natural healing cycles.
Incorporating Mushroom Cocoa Into Your Routine
Incorporating mushroom cocoa into your daily routine is easy and versatile. Here are some of the best ways to enjoy it:
- Beverages: The most popular way to enjoy mushroom cocoa is as a warm drink. Simply mix with hot water, milk, or your favorite milk alternative for a calming, recovery-focused drink.
- Smoothies: Add mushroom cocoa to your smoothies for a nutrient-packed boost. It pairs well with fruits, greens, and protein powders for a delicious, wellness-enhancing blend.
-
Baking: Substitute mushroom cocoa for regular cocoa powder in your baking recipes. Keep in mind that the unique, earthy flavor may alter the taste, but it can add depth to chocolate-based treats while still offering the health benefits of the mushrooms.
These are just a few ideas to help you incorporate mushroom cocoa into your day, whether you’re winding down at night or adding a nutrient boost to your breakfast.
Final Thoughts: Is Mushroom Cocoa the Ultimate Power Drink?
Choosing between regular and mushroom cocoa depends on what you’re looking for—the most beneficial cocoa stays close to its natural form, preserving antioxidants and key nutrients. Minimally processed options like raw cacao powder or nibs keep more of what makes the cacao bean effective.
Mushroom cocoa builds on that foundation, combining cacao with functional mushrooms to support stress response, recovery, and overall well-being. A small shift—designed to do more.
FAQ
What Distinguishes Cacao From Cocoa?
Cacao refers to the raw, unprocessed beans from the cocoa bean of the Theobroma cacao tree. In contrast, cocoa is made from beans that have been roasted and processed. Due to its minimal processing, cacao retains more of its natural cocoa compounds, including antioxidants and nutrients, making it a more nutrient-dense option.
Which Form of Cocoa Is Considered the Healthiest?
Minimally processed forms of cocoa, such as raw cacao powder and cacao nibs, are often considered the healthiest because they preserve more antioxidants and essential minerals. These options are closer to the natural cocoa bean and offer a richer nutrient profile than more refined products like milk chocolate or highly processed dark chocolate.
How Does Processing Impact Cocoa’s Nutritional Value?
Processing methods, such as roasting and alkalization, can degrade certain beneficial compounds in cocoa, including flavanols, which are known for their heart health benefits. Less processed forms of cocoa, such as raw cacao, retain more of these natural cocoa compounds, making them a healthier choice.
What Are the Potential Benefits of Mushroom Cocoa?
Mushroom cocoa pairs the rich, comforting taste of dark chocolate with the health-boosting benefits of medicinal mushrooms. These mushrooms, such as Reishi and Tremella, may support stress resilience, enhance recovery, and promote hydration. The addition of mushrooms can offer a unique boost to overall wellness, making it a great alternative for those looking to go beyond traditional milk chocolate.
Where Can I Find Mushroom Cocoa in the UK?
Look for organic mushroom cocoa online or at health-focused retailers like Planet Organic or Holland & Barrett. MOGU’s Cacao PM blend offers a UK-formulated option featuring ceremonial-grade cacao and complementary functional mushrooms such as Reishi, Tremella, and Poria.
About MOGU
At MOGU, we believe nature’s intelligence doesn’t need to be reinvented—just reconnected with. We explore the intersection of mushrooms, function, and modern living through thoughtful design, the latest science, and a deep respect for nature.
What you take in shapes how you think, feel, and move through the world. We’re here to build a deeper connection between the everyday and the elemental, starting with mushrooms.
This is just the beginning.
The studies referenced in this article relate to the individual ingredients discussed and are provided for informational purposes only. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Individual results may vary. Always consult a healthcare professional before introducing any new supplement into your routine.